Diesel Cycle
Processes of Ideal Diesel Cycle
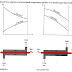
The ideal Otto cycle comprises of two isentropic, one constant volume, and one constant pressure processes. The Diesel cycle is an open cycle or non-cyclic process since the fresh air and fuel is inducted inside the engine during each cycle and the burnt mixture is released to the atmosphere To understand these processes let us consider piston and cylinder engine with air and diesel as the working fluid. Refer the P-V diagram given at the bottom.
1) Air intake process 1-2: During this process the inlet valve of the engine is open, the piston moves towards the bottom position inducting air at constant pressure.
2) Isentropic compression process 2-3: During this process the inlet and exhaust valves of the engine remain close and the air, which has been inducted inside the cylinder, is compressed to the minimum volume. The compression ratio of air is between15 to 20. High compression ratios are very important in the Diesel cycle as we it increases the efficiency of the cycle also allows uniform burning of fuel.
3) Injection of fuel and its combustion at constant pressure 3-4: During this process the fuel valve opens and fuel is injected inside the cylinder consisting of hot air at high pressure. After injection the combustion of fuel takes place instantly. Since the combustion of fuel occurs due to high pressure, the diesel engine is also called Compression Ignition engine. Due to combustion fuel high pressure and temperature is generated.
4) Isentropic expansion process 4-5: Due to extremely high pressure, the piston is pushed again towards the bottom most position of the cylinder. It is during this process that the actual work is produced from the engine.
5) Constant volume heat rejection process 5-6: During this process the exhaust valve opens and all the exhaust gases are ready to be released to the atmosphere. The pressure inside the cylinder falls drastically.
6) Exhaust process 6-1: During this process the exhaust valve is open and the piston moves upwards and removes all the exhaust gases inside the cylinder at constant pressure.
Thereafter the exhaust valve closes, the piston starts moving in downward direction, the inlet valve opens and fresh air-fuel mixture is inducted. The whole cycle is completed in four strokes of engine, hence it is called four-stroke engine.





1 comments:
very interesting, good job and thanks for sharing such a good blog.
Reverse treatment plant
Post a Comment